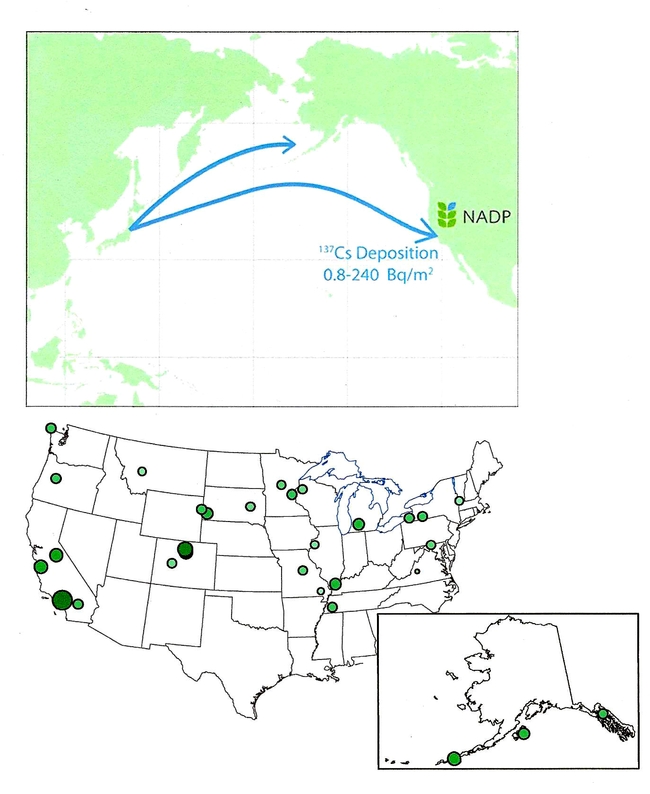
The UC Hopland Research & Extension Center has one of two National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) sites in the UC system that weekly monitors precipitation quality. Using the structure of the NADP, the US Geological Survey (USGS) looked at numerous measurements of radionuclide wet depositions over North America from over 167 NADP sites before and after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station incident of March 12, 2011. I am not sure if the UC-HREC CA-45 NADP site was one of the selected sample sites.
From the period of time from March 12 through April 5, 2011, wet-only precipitation samples were analyzed for fission-product isotopes, and variable amounts of Iodine 131, Cesium 134, and Cesium 137 were detected at about 21% of the sampled NADP sites. Radioactive iodine and cesium are often some of the largest contributors to human radiation doses after a nuclear reactor accident.
The bottom map shows NADP sites where the USGS detected 137 Cesium in rainwater samples. The dot size shows relative deposition amounts. Fallout amounts measured in these samples were well below any level of public concern.
Methods and results of the study are documented in USGS Open-File Report 2011-1277.